Work with Docker containers
The Docker API implementation on Triton runs parallel with Triton's own CloudAPI, and the containers you provision using the Docker API run along side the infrastructure containers and hardware VMs you can start using CloudAPI.
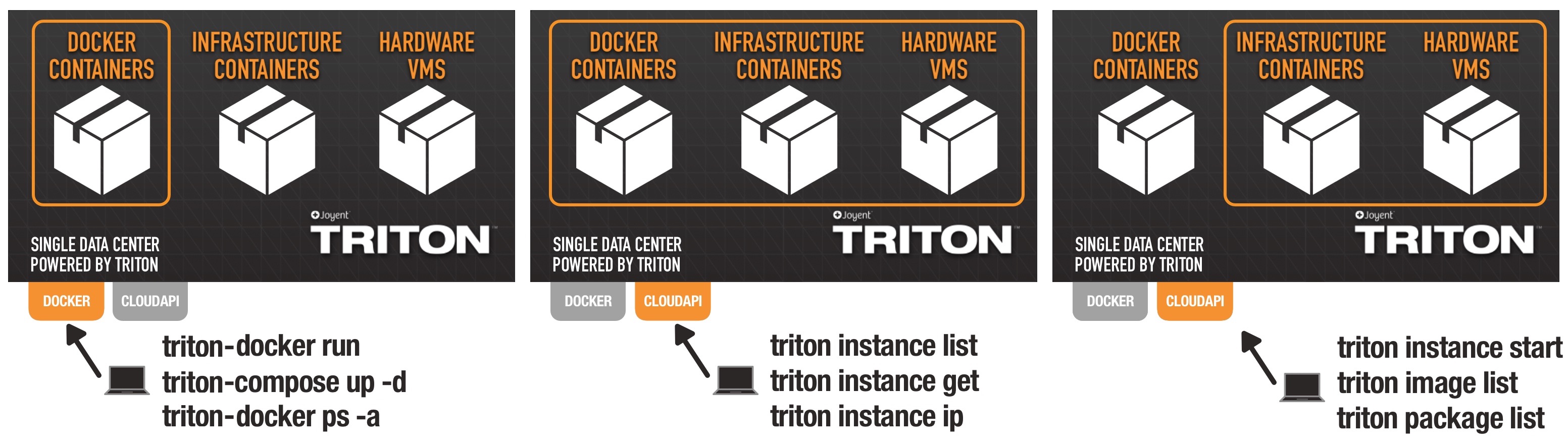
On Triton, you can have a single view of your bare-metal Docker containers, infrastructure containers, and hardware VMs.
and Triton
Once docker has been installed, you'll be able to run containers on Triton. Get started:
- Start and run a Docker container
- Start multiple containers with Docker Compose
- Pull new images
- Get private Docker images
- List your containers
- Inspect your containers
- Get your IP address
- Run commands in a shell
- Stop and remove containers
Docker commands and options to avoid
Triton Elastic Docker Host supports most of the features of Docker's 1.22 spec. That means you can do most everything you'd expect to do, but there are a few exceptions:
docker build ...: we advise you build your Docker images in your local environment or using the Docker daemon on an HVM instance. Our focus is on making the Triton Elastic Docker Host the best place to run your Docker images; building Docker images using the Triton Elastic Docker Host is not supported.docker network...: Triton supports rich networks unlike any you'll be able to create with Docker, but you'll have to use CloudAPI to create them for now. Take a look at the networks section, above- Docker Compose file format 2+: technically this works now if you define
network_mode: bridge. Your containers won't actually be using bridge networking, but it's a workaround until we implement support for managing Triton networks using thedocker network...commands; see networks, above docker volume...: This family of commands in Docker is probably an anti-pattern that turns Docker hosts into pets, but take a look at the volumes section abovedocker service...: this family of commands seems to finally be taking shape in the most recent Docker release; Triton will offer Triton will offer comparable features in 2017docker events...: there are no plans to implement this feature
Comparing Docker API and CloudAPI/Triton CLI commands
Docker API access on Triton works in parallel with CloudAPI. Many Docker API commands (which use the Docker CLI tool) have equivalent commands in CloudAPI (which uses the Triton CLI).
| Purpose | Docker API | CloudAPI |
|---|---|---|
| List containers | docker ps |
triton instances or triton instance list |
| Get details for container by name or UUID | docker inspect <name or UUID> |
triton instance get <name or UUID> |
| Get IPs for container | --format '{{ .NetworkSettings.IPAddress }}' <name or UUID> or docker inspect <name or UUID> | json -aH NetworkSettings |
triton instance ip <name or UUID> or triton instance get -j <name or UUID> | json primaryIp |
| Create and start a new container | docker run <image name> |
triton instance create <image name or UUID> <package name or UUID> |
| Create, but don't start, a container | docker create <image name> |
Not supported in CloudAPI |
| Start a stopped container | docker start <name or UUID> |
triton instance start <name or UUID> |
| Restart a container | docker restart <name or UUID> |
triton instance reboot <name or UUID> |
| Stop a container | docker stop <name or UUID> |
triton instance stop <name or UUID> |
| Remove container | docker rm <name or UUID> |
triton instance delete <name or UUID> |
| Stop and remove all containers (use with great caution) | docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q) |
triton instance delete $(triton instances -Ho shortid) |
| Get shell in a container1 | docker exec -it <name or UUID> bash |
triton ssh <name or UUID> |
| List images | docker images |
triton images or triton image list |
| Get image history/layers | docker history <name or UUID> |
--- |
| Get image metadata | Not supported in Docker | triton image get <image UUID> |
| Import/download a new image | docker pull <name or UUID> |
--- |
| Remove an image from user's view | docker rmi <name or UUID> |
--- |
| Permanently delete an image2 | --- | triton image delete <image UUID> |
-
Technically, the Docker command is using the Docker API to execute an appliction (
bashin this case) inside the container and passing the input and output via Docker API to your local shell. The Triton CLI example here is a convenience for starting SSH in your local shell, and all communication is via normal SSH. ↩ -
You can only delete your custom images, not any of MNX's pre-created images. ↩
