Managing instances
This page describes how to manage both containers and hardware virtual machines in Triton.
Finding instances
You can list and find instances on a compute node by using a few different methods:
- Using the Operations Portal
- Using the API from the head node (
cnapiorvmapi) - Running vmadm(1m) from the compute node
- Running
sdc-vmadmfrom the head node
List and find instances using the Operations Portal
To view a list of all instances using the Operations Portal, log in to the Operations Portal dashboard (https://x.x.x.x, where x.x.x.x = the Operations Portal IP), and select Virtual Machines.
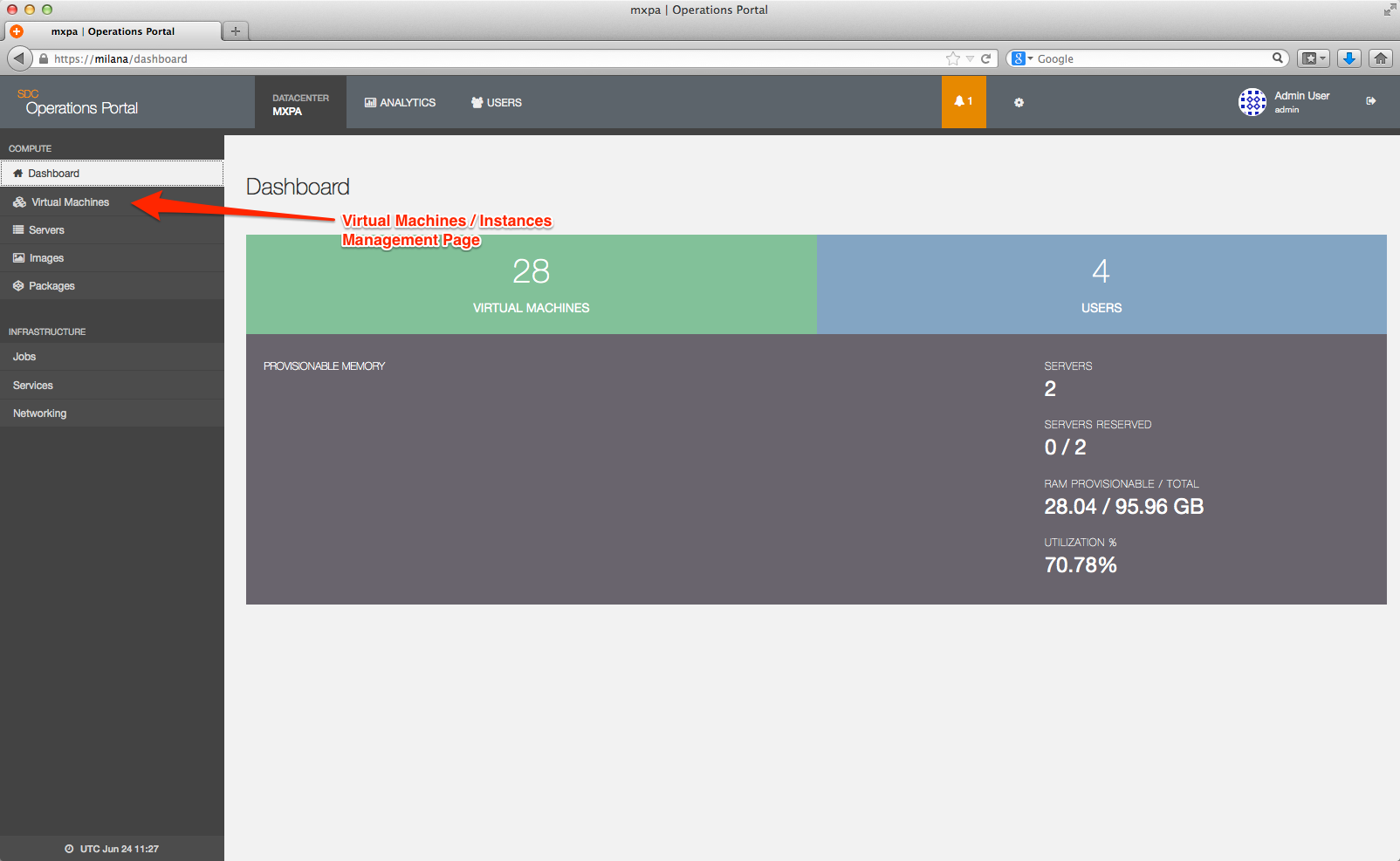
The Virtual Machines instance management page displays:
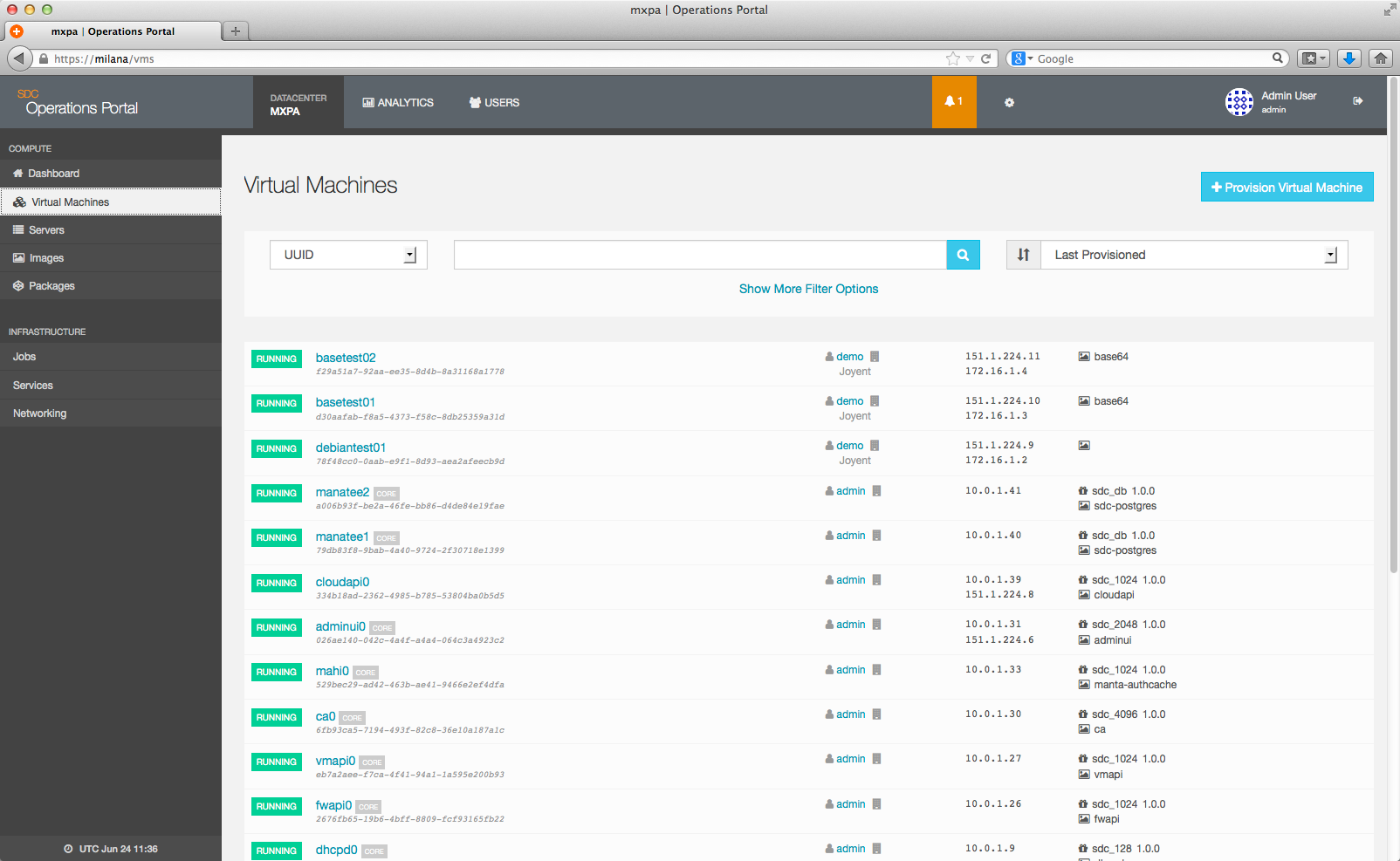
You can search for specific instances by filtering your options based on instance UUID, Owner UUID, the package name, IP, or alias:
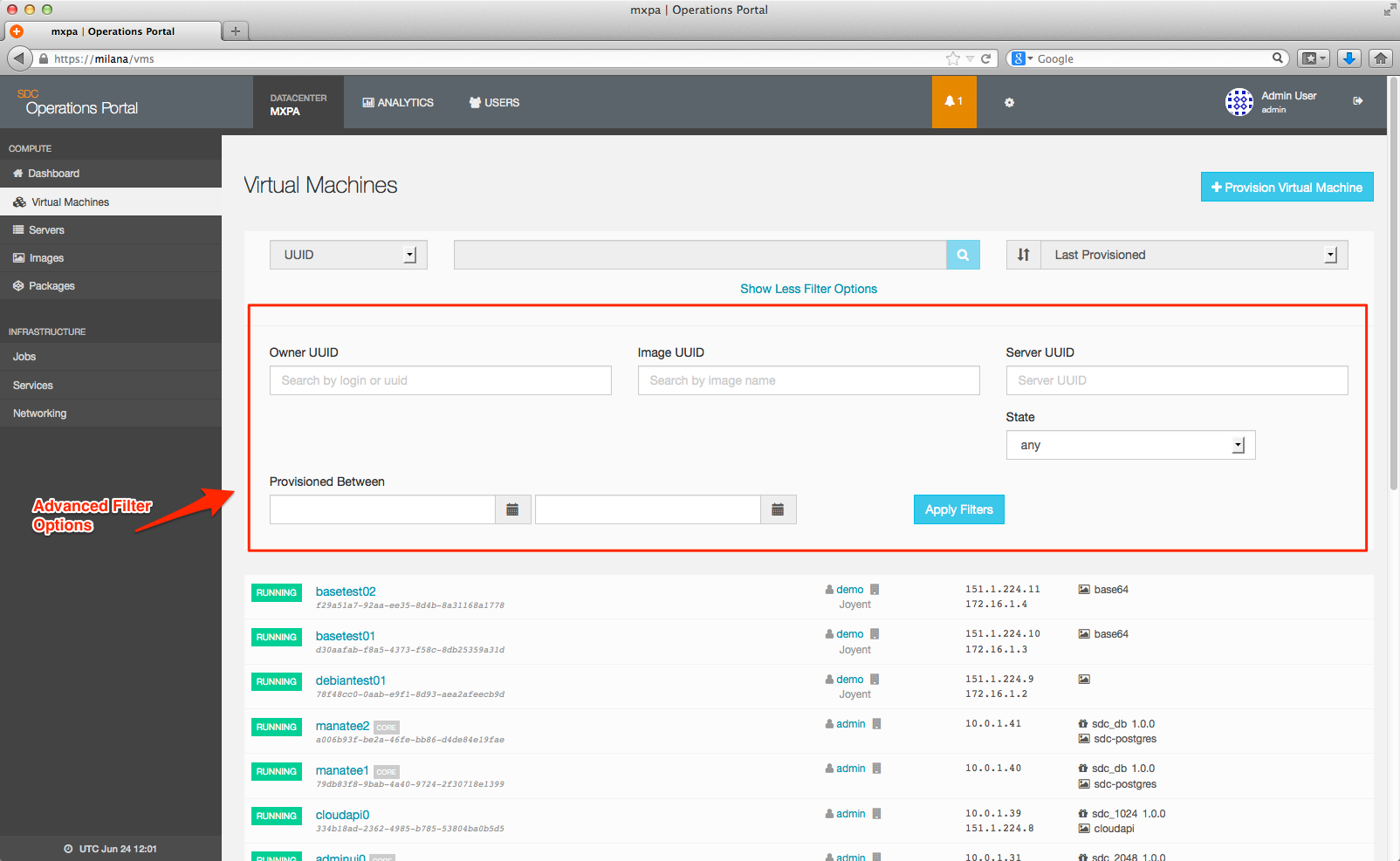
Click the Show More Filter Options link to add additional filters:
To view a list of instances that are on specific compute nodes, from the left nav, select Servers:
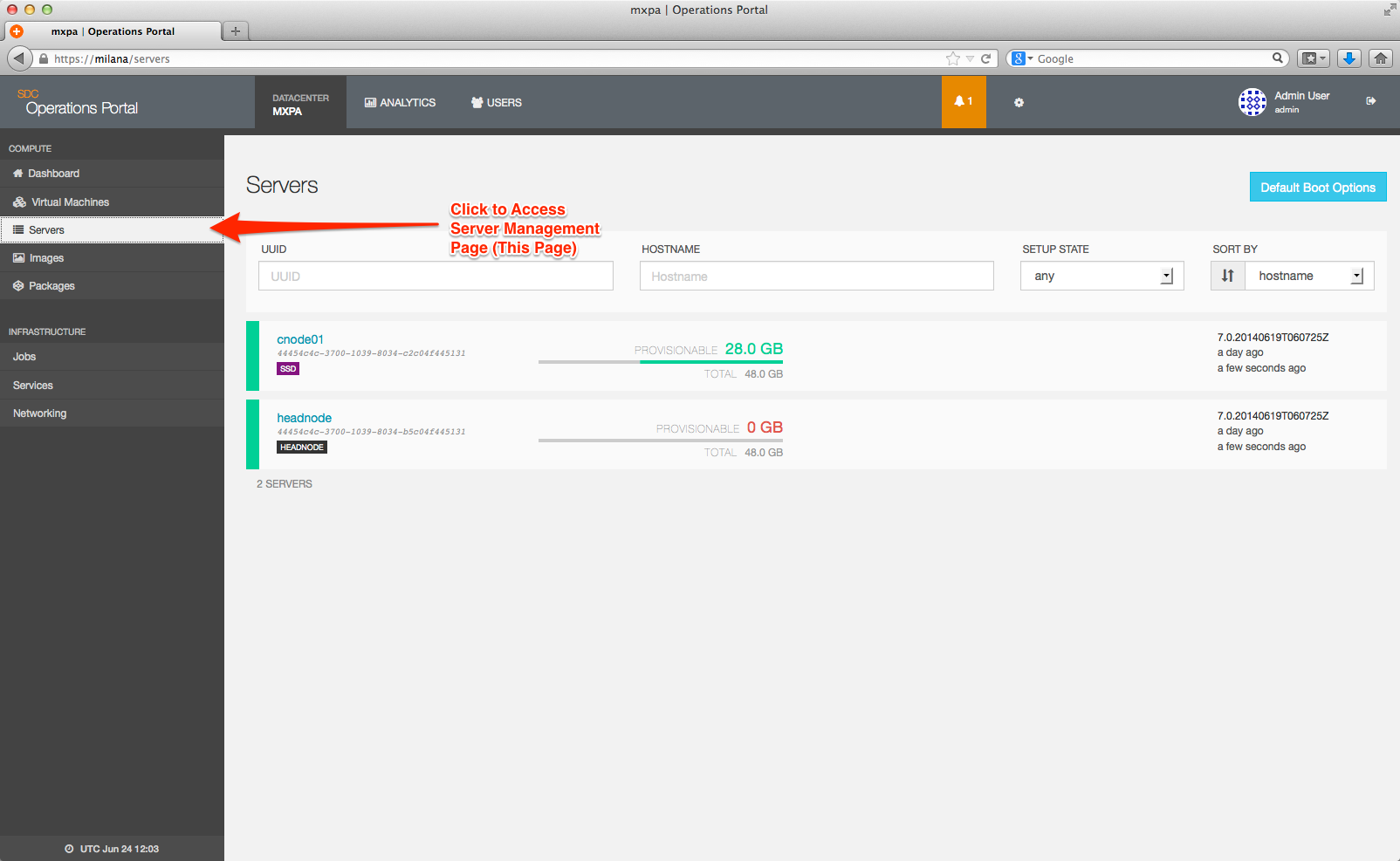
A list of all compute nodes displays. Similar to filtering instances, you can also search for compute nodes by UUID or hostname. You also have the option to sort your results.
Click on the compute node you want to view, and then scroll down to the bottom to view a list of all instances that are configured on that server:

List and find instances from the head node
From the head node, you can use sdc-cnapi and sdc-vmapi to view and find instances.
sdc-cnapi
Use sdc-cnapi to list instances on a specific compute node:
headnode# sdc-cnapi /servers/:server_UUID/vmsExample usage and output:
headnode# sdc-cnapi /servers/44454c4c-3700-1039-8034-c2c04f445131/vms
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 1531
Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 18:24:31 GMT
Server: Compute Node API
x-request-id: b8949880-aadc-11e3-8179-252185cd5c37
x-response-time: 7
x-server-name: 4646badf-098a-41ba-b9ab-e3e06946d6e9
Connection: keep-alive
[
{
"uuid": "d8f99863-b45a-c1a4-df12-ca98347c2bd4",
"owner_uuid": "b43bd06c-88f9-647c-ffc1-82d02287e396",
"quota": 25,
"max_physical_memory": 256,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent",
"cpu_cap": 150,
"last_modified": "2014-03-12T13:58:13.000Z"
},
{
"uuid": "8d44d9e9-fa70-462e-b355-02b077e8556c",
"owner_uuid": "930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853",
"quota": 50,
"max_physical_memory": 2048,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent-minimal",
"cpu_cap": 400,
"last_modified": "2014-03-13T15:59:37.000Z"
},
{
"uuid": "15161bd5-a5c4-40f7-967e-d3b9f6ec64fd",
"owner_uuid": "930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853",
"quota": 25,
"max_physical_memory": 8192,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent-minimal",
"cpu_cap": 400,
"last_modified": "2014-03-13T15:59:38.000Z"
},
{
"uuid": "fd44546b-154d-6098-e96d-88805c802270",
"owner_uuid": "b43bd06c-88f9-647c-ffc1-82d02287e396",
"quota": 25,
"max_physical_memory": 256,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent",
"cpu_cap": 150,
"last_modified": "2014-03-12T15:49:57.000Z"
},
{
"uuid": "f12ecbd6-b615-eb7d-c0b8-94df68378932",
"owner_uuid": "b43bd06c-88f9-647c-ffc1-82d02287e396",
"quota": 25,
"max_physical_memory": 256,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent",
"cpu_cap": 150,
"last_modified": "2014-03-12T15:57:41.000Z"
},
{
"uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"owner_uuid": "99af3f22-a669-eec0-99f1-d35af19735ac",
"quota": 25,
"max_physical_memory": 256,
"zone_state": "running",
"state": "running",
"brand": "joyent",
"cpu_cap": 150,
"last_modified": "2014-03-13T15:55:06.000Z"
}
]sdc-vmapi
You can also use sdc-vmapi to obtain a list of instances and their state, by compute node:
headnode# sdc-vmapi /vms?server_uuid=[server_UUID] | json -aH uuid state aliasExample usage and output:
# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms?server_uuid=44454c4c-3700-1039-8034-c2c04f445131 | json -aH uuid state alias
d8f99863-b45a-c1a4-df12-ca98347c2bd4 running test0
fd44546b-154d-6098-e96d-88805c802270 running test1
8d44d9e9-fa70-462e-b355-02b077e8556c running manatee1
15161bd5-a5c4-40f7-967e-d3b9f6ec64fd running moray1
f12ecbd6-b615-eb7d-c0b8-94df68378932 running c426b37
4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7 running feetwins-base
vmadm
Listing instances from a compute node is done by using the vmadm command.
To list all instances, run the following:
computenode# vmadm listExample usage and output:
computenode# vmadm list
d8f99863-b45a-c1a4-df12-ca98347c2bd4 running test0
fd44546b-154d-6098-e96d-88805c802270 running test1
8d44d9e9-fa70-462e-b355-02b077e8556c running manatee1
15161bd5-a5c4-40f7-967e-d3b9f6ec64fd running moray1
f12ecbd6-b615-eb7d-c0b8-94df68378932 running c426b37
4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7 running feetwins-basesdc-oneachnode
Alternatively, you can invoke the use of vmadm list by using sdc-oneachnode:
headnode# sdc-oneachnode -n [server_hostname] vmadm listExample usage and output:
headnode# sdc-oneachnode -n 78-2b-cb-0a-75-23 vmadm list
=== Output from 44454c4c-3700-1039-8034-c2c04f445131 (78-2b-cb-0a-75-23):
UUID TYPE RAM STATE ALIAS
4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7 OS 256 running feetwins-base
d8f99863-b45a-c1a4-df12-ca98347c2bd4 OS 256 running test0
f12ecbd6-b615-eb7d-c0b8-94df68378932 OS 256 running c426b37
fd44546b-154d-6098-e96d-88805c802270 OS 256 running test1
8d44d9e9-fa70-462e-b355-02b077e8556c OS 2048 running manatee1
15161bd5-a5c4-40f7-967e-d3b9f6ec64fd OS 8192 running moray1Starting, stopping, rebooting, and resizing an instance
There are multiple ways to start, stop, reboot, and resize instances:
- From the Operations Portal
- VMAPI from the head node
vmadmfrom the compute nodesdc-vmadmfrom the head node
Using the Operations Portal
To start, stop, or reboot a instance from the Operations Portal:
- Search for the instance in the Operations Portal.
- On the instance page, click the Actions drop down menu and select an action.
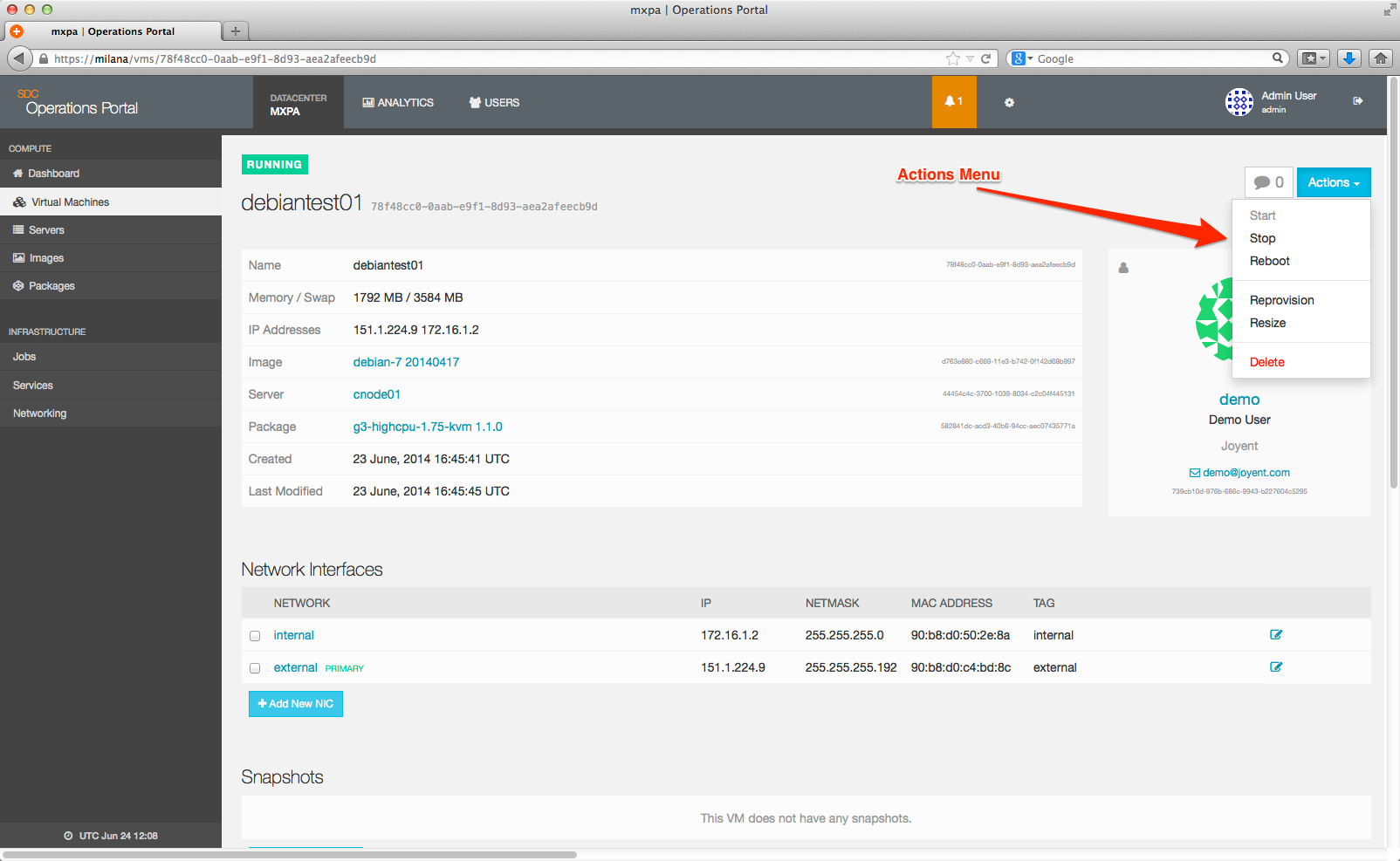
The actions that you can take include:
- Start starts a instance that is in a stopped state. This option will not be available if the instance is running.
- Stop shuts down an instance that is in a running state. This option will not be available if the instance is stopped.
- Reboot restarts an instance. This option will not be available if the instance is stopped.
- Delete destroys the current instance, pending confirmation. This will result in the loss of data in the instance.
- Resize allows you to resize your SmartOS, Docker, and byhve based instances to a different package. This option is not available for KVMs.
-
Reprovision reprovisions the instance using the same configuration that it is currently running with in terms of package and image.
Warning: Once an instance is deleted or reprovisioned, will result in a loss of data. Yyou can not recover it. Proceed with caution when choosing these actions.
Resizing
You also have the option to resize instances. Selecting the Resize option opens a dialog that prompts you to change the vm package to meet your resizing needs:

Resizing is only supported on containers running SmartOS, Docker, bhyve, or Container Native Linux (LX Branded Zones) at this time, but not for KVMs. KVM virtualized containers require a new container to be provisioned on the new package, then a migration of the data from the original to new instance.
Important: If you are resizing a container running SmartOS or Container Native Linux to a smaller package, it is important to confirm that the current disk usage is less then the target disk quota.**
To learn more about resizing, see when to resize an instance.
Using VMAPI from the head node
Stopping an instance
To stop an instance from the head node using vmapi, the command is:
headnode# sdc-vmapi /vms/:uuid?action=stop -X POSTExample usage and output
headnode# sdc-vmapi /vms/4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7?action=stop -X POST
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 100
Content-MD5: 2H5pF4zDrchjU1Ugv5nKWA==
Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 04:45:00 GMT
Server: VMAPI
x-request-id: 66de3fd0-ab33-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5
x-response-time: 35
x-server-name: 069caca7-94dc-4ebb-9579-cc223e44d3ab
Connection: keep-alive
{
"vm_uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"job_uuid": "4e2b1a79-6b46-4576-a0ce-36501729509e"
}Should the command be accepted, you'll see a job_uuid has been created for the stop action, as shown in the above output. You can view the progress and outcome of this job from the Operations Portal by navigating to:
You can also view the details of a job using sdc-vmapi from the head node (example below for the job example from above):
headnode# sdc-vmapi /jobs/4e2b1a79-6b46-4576-a0ce-36501729509e
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 1821
Content-MD5: fpRPqOfJW5+mxvla82Go7w==
Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 04:52:31 GMT
Server: VMAPI
x-request-id: 7380b230-ab34-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5
x-response-time: 9
x-server-name: 069caca7-94dc-4ebb-9579-cc223e44d3ab
Connection: keep-alive
{
"name": "stop-7.0.4",
"uuid": "4e2b1a79-6b46-4576-a0ce-36501729509e",
"execution": "succeeded",
"params": {
"task": "stop",
"vm_uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"owner_uuid": "99af3f22-a669-eec0-99f1-d35af19735ac",
"server_uuid": "44454c4c-3700-1039-8034-c2c04f445131",
"current_state": "running",
"x-request-id": "66de3fd0-ab33-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5",
"jobid": "4e2b1a79-6b46-4576-a0ce-36501729509e"
},
"exec_after": null,
"created_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:00.899Z",
"timeout": 530,
"chain_results": [
{
"result": "All parameters OK!",
"error": "",
"name": "common.validate_params",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:06.181Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:06.276Z"
},
{
"result": "Request has been setup!",
"error": "",
"name": "common.setup_request",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:06.291Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:06.385Z"
},
{
"result": "OK",
"error": "",
"name": "cnapi.acquire_vm_ticket",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:06.400Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:09.822Z"
},
{
"result": "OK",
"error": "",
"name": "cnapi.wait_on_vm_ticket",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:09.840Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.133Z"
},
{
"result": "VM is running",
"error": "",
"name": "common.ensure_vm_state",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.148Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.461Z"
},
{
"result": "Task queued to CNAPI!",
"error": "",
"name": "cnapi.stop_vm",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.476Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.738Z"
},
{
"result": "Job succeeded!",
"error": "",
"name": "cnapi.poll_task",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:10.752Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:16.814Z"
},
{
"result": "VM is now stopped",
"error": "",
"name": "vmapi.check_state",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:16.827Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:19.893Z"
},
{
"result": "OK",
"error": "",
"name": "cnapi.release_vm_ticket",
"started_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:19.924Z",
"finished_at": "2014-03-14T04:45:20.234Z"
}
]
}
Starting an instance
To start an instance using sdc-vmapi, run:
headnode# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/:uuid?action=start -X POSTExample usage and output:
# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7?action=start -X POST
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 100
Content-MD5: G0SIUMSwiu6vv9rZJQ6iuw==
Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 04:48:08 GMT
Server: VMAPI
x-request-id: d6e72080-ab33-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5
x-response-time: 29
x-server-name: 069caca7-94dc-4ebb-9579-cc223e44d3ab
Connection: keep-alive
{
"vm_uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"job_uuid": "82acee52-2b5b-41d9-a4e3-02a626554870"
}Rebooting an instance
To reboot an instance from the head node, run:
headnode# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/:uuid?action=reboot -X POSTExample usage and output:
# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7?action=reboot -X POST
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 100
Content-MD5: F/gVcFwEOqjUq/7sIK2RkA==
Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 04:56:26 GMT
Server: VMAPI
x-request-id: ff91c840-ab34-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5
x-response-time: 29
x-server-name: 069caca7-94dc-4ebb-9579-cc223e44d3ab
Connection: keep-alive
{
"vm_uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"job_uuid": "68fb03fd-84f2-4089-8d9d-54a3e8815c58"
}
Resizing an instance
To resize an instance from the head node, use the update action as shown below:
headnode# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/:uuid?action=update -d '{"billing_id":"package_uuid", "package_name":"[package_name]"}'Example usage and output
headnode# sdc sdc-vmapi /vms/4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7?action=update -d '{"billing_id":"73a1ca34-1e30-48c7-8681-70314a9c67d3", "package_name":"sdc-128"}'
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 100
Content-MD5: UNKK4R8kus+KQtJrkg07hA==
Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 04:59:16 GMT
Server: VMAPI
x-request-id: 64b644d0-ab35-11e3-80c0-d1d28a191fe5
x-response-time: 32
x-server-name: 069caca7-94dc-4ebb-9579-cc223e44d3ab
Connection: keep-alive
{
"vm_uuid": "4985f9fb-e674-e472-ac02-86e15242d6f7",
"job_uuid": "923d7561-ca9e-4b3b-8947-d9061e9ae169"
}Using vmadm from the compute node
Stopping, starting, and rebooting an instance from a compute node is done by using the vmadm command. You can learn more about vmadm by viewing the man pages or by clicking on the following link vmadm(1m) .
Migrating instances between compute nodes
Currently, the supported way of moving instances between compute nodes is to provision a new instance and migrate the data/application as required. Since this is not always feasible, it is possible to migrate instances between compute nodes by following the procedure outlined at migrating instances between compute nodes.
Please be aware that the migration of instances between compute nodes is not a supported process, and the procedure linked above is provided as-is. It is recommended to reprovision when an instance needs to be moved to a new compute node. You assume all risks responsible when utilizing this process; MNX is not responsible for any loss or damage caused by using this procedure.
Using delegated datasets
It is possible to enable a container running SmartOS for delegated dataset support. The procedure using delegated datasets will provide instructions on creating an instance with delegated dataset support as well as how to create, import, and export delegated datasets within the context of that instance.
Using the metadata API
The Metadata API is a lightweight interface that lets your machine get data from its Triton record. For more information and usage examples, please see using the Metadata API.
