Cloud firewall logging
Joyent introduces Cloud firewall logging (CFW) with PI20190705. This new feature adds two new components, the firewall-logger-agent and the logarchiver-agent. Joyent developed the Cloud firewall logging as an answer to customer requests for logging inbound connections as required by Korean law.
Triton firewall logging
The firewall-logger-agent captures the blocking attempts against firewall rules that have logging enabled by the end user using Triton CLI tools.
The log captures three events: block, begin, and end. The logs are stored as JSON files on a per-instance or virtual machine (VM) basis. In the event of insufficient disk space or other conditions, log entries may be dropped.
Manta is strongly recommended for cloud firewall logging. However, end users who do not have an on-premise Manta can use the firewall-logger-agent to generate logs and use shell program(s) and Cron job(s) to store and maintain logs.
Triton log archiver
The logarchiver-agent is a service that includes its own hermes instance. This instance then deploys its own logarchiver-agent, which runs in parallel with hermes-agent on the compute nodes (CN). Log files are collected from each CN every hour and automatically uploaded to Manta. Once Hermes has stored the file in Manta, Hermes removes it from the CN.
Log location
cfwlogd logs are stored in two locations:
- The CN in
/var/log/firewall - The customer's Manta in
/:customer_login/reports/firewall-logs/:year/:month/:day/:vm_uuid/:iso8601stanp.log.gz
Log retention
Triton does not automatically remove old log files in the Manta reports directory. Customers can decide when to remove expired logs.
For customers without an on-prem Manta, any file in /var/log/firewall/*/* on the CN that reaches seven days old (find -mtime +7) will be removed.
Log rotation
When cfwlogd receives a signal hand up (SIGHUP), it closes all log files and reopens them on demand. The expectation is that a SIGHUP will be delivered on a regular (e.g. hourly) basis by logadm.
logadm should be configured to periodically rotate all current .log files found in /var/log/firewall/*/* to :iso8601stamp.log.gz.
Record formatting
Each log entry is a JSON object, stored on a single line with no extra white space. The content format of record looks something like the following example where each bracket { } is one event.
[root@headnode (swdemo05) /var/log/firewall/930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853/3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86]# cat 2019-08-15T01:00:01.log
{"event":"begin","source_port":2048,"destination_port":0,"protocol":"ICMP","direction":"in","source_ip":"::ffff:13.231.120.57","destination_ip":"::ffff:64.30.138.134","timestamp":"2019-08-15T00:00:24.192603Z","rule":"41c823cf-97da-43a3-82c2-891756dbe105","vm":"3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86","alias":"imgapi0"}
{"event":"begin","source_port":2048,"destination_port":0,"protocol":"ICMP","direction":"in","source_ip":"::ffff:52.69.153.168","destination_ip":"::ffff:64.30.138.134","timestamp":"2019-08-15T00:00:32.872840Z","rule":"41c823cf-97da-43a3-82c2-891756dbe105","vm":"3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86","alias":"imgapi0"}
{"event":"begin","source_port":2048,"destination_port":0,"protocol":"ICMP","direction":"in","source_ip":"::ffff:3.112.243.54","destination_ip":"::ffff:64.30.138.134","timestamp":"2019-08-15T00:01:01.651496Z","rule":"41c823cf-97da-43a3-82c2-891756dbe105","vm":"3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86","alias":"imgapi0"}
...For clarity, JSON records can be passed through Bunyan for easier readability. The pretty-printed log entry for a typical allowed/denied connection looks similar to this easy-to-read example:
{
"event": "begin", OR (“block’)
"protocol": "TCP",
"direction": "in",
"source_port": 1234,
"destination_port": 22,
"source_ip": "::ffff:192.168.128.12",
"destination_ip": "::ffff:192.168.128.5",
"timestamp": "2019-05-02T14:27:32.104586532Z",
"rule": "43854efd-976b-485c-9e79-6f4e94eba8fd",
"vm": "473b158d-023c-c4f7-9785-b027275580c9",
"alias": "cfw-test-1"
}Installing cloud firewall logging agents
To install the firewall-logger-agent, set the channel:
sdcadm channel set releaseTo install the firewall-logger-agent, run:
sdcadm post-setup firewall-logger-agentTo check health, run:
sdcadm health firewall-logger-agentTo install the logarchiver-agent, run:
sdcadm post-setup logarchiverTo check for the firewall directory, run:
cd /var/log/firewallIf /var/log/firewall does not exist, simply create it.
Enabling firewall rules in the Admin Portal
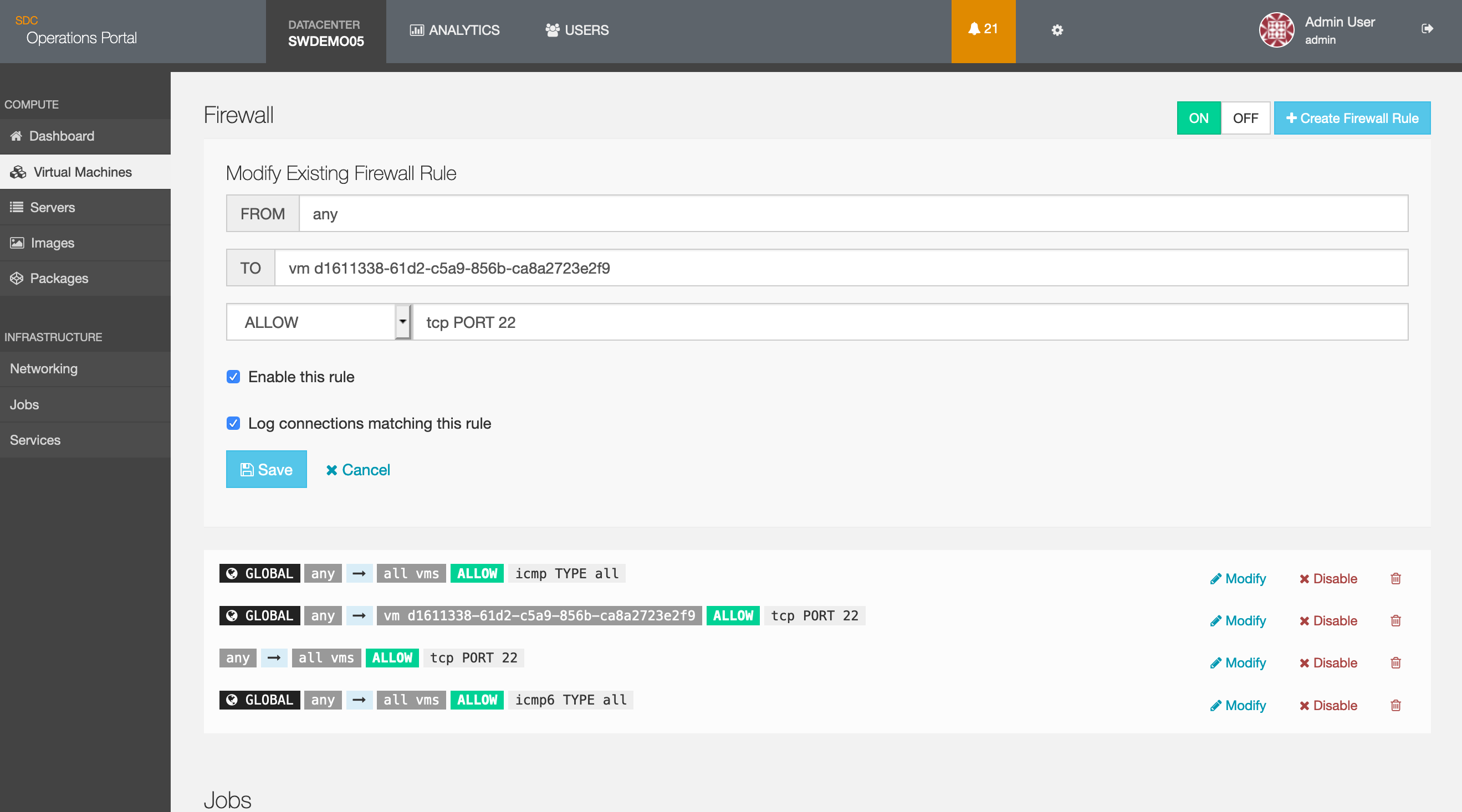
You must enabling logging for each connection on a per rule per instance basis via the Admin portal.
In the Admin portal, navigate to Virtual Machines and select Firewall. For each rule, modify the existing firewall rules by selecting the Enable this rule and Log connections matching this rule check boxes:
Enabling firewall rules using Triton CLI
Cloud firewall can also be enabled by the end user via the Triton CLI by adding the -l or --log flag to the existing triton fwrule create command. For example:
# triton -i fwrule help create
Create a firewall rule.
Usage:
triton fwrule create [OPTIONS] RULE-TEXT
Options:
-h, --help Show this help.
-j, --json JSON stream output.
-l, --log Enable logging of new TCP connections or new
other-protocol sessions matching this rule.
-d, --disabled Disable the created firewall rule. By default a created
firewall rule is enabled. Use "triton fwrule enable" to
enable it later.
-D DESC, --description=DESC
Description of the firewall rule.
# Allow SSH access from any IP to all instances in a datacenter.
triton fwrule create -D "ssh" "FROM any TO all vms ALLOW tcp PORT 22" -l
# Allow SSH access to a specific instance.
triton fwrule create \
"FROM any TO vm ba2c95e9-1cdf-4295-8253-3fee371374d9 ALLOW tcp PORT 22" --logOnce enabled, the log collection process should start collecting events.
Note: At this time, is it not possible to enable cloud firewall logging from the Triton Service portal (if installed).
Monitoring log collection
The process can be monitored as shown using the following example commands:
[root@headnode (swdemo05) /var/log/firewall]# ls -al
total 13
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 3 Aug 7 03:29 .
drwxr-xr-x 13 root sys 74 Aug 14 08:00 ..
drwxr-xr-x 3 root daemon 3 Aug 7 03:29 930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853
[root@headnode (swdemo05) /var/log/firewall]# cd 930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853[root@headnode (swdemo05) /var/log/firewall/930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853]# ls -al
total 11
drwxr-xr-x 3 root daemon 3 Aug 7 03:29 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 3 Aug 7 03:29 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root daemon 171 Aug 15 05:00 3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86[root@headnode (swdemo05) /var/log/firewall/930896af-bf8c-48d4-885c-6573a94b1853/3c88c938-dc1b-431c-80bc-91e602e2aa86]# ls -al
total 7
drwxr-xr-x 2 root daemon 171 Aug 15 05:00 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root daemon 3 Aug 7 03:29 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root daemon 569 Aug 8 06:00 2019-08-08T06:00:00.log.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root daemon 343 Aug 8 07:00 2019-08-08T07:00:00.log.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root daemon 437 Aug 8 08:00 2019-08-08T08:00:01.log.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root daemon 288 Aug 8 09:00 2019-08-08T09:00:00.log.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root daemon 0 Aug 15 05:00 current.log